So a U of Chicago economist and ajournalist get together to write a book called "Superfreakanomics"
It has a chapter on gobal warming that is so full of BS it hurts.
Lots of great takedown on the web about it, but this has to be the best.
From a U of Chicago colleague no less. World class pwnage here.
and he does 
ending with a Google map of how to get to his office to ask questions:
It has a chapter on gobal warming that is so full of BS it hurts.
Lots of great takedown on the web about it, but this has to be the best.
From a U of Chicago colleague no less. World class pwnage here.
...
I am addressing this to you rather than your journalist-coauthor because one has become all too accustomed to tendentious screeds from media personalities (think Glenn Beck) with a reckless disregard for the truth. However, if it has come to pass that we can’t expect the William B. Ogden Distinguished Service Professor (and Clark Medalist to boot) at a top-rated department of a respected university to think clearly and honestly with numbers, we are indeed in a sad way.
By now there have been many detailed dissections of everything that is wrong with the treatment of climate in Superfreakonomics , but what has been lost amidst all that extensive discussion is how really simple it would have been to get this stuff right. The problem wasn’t necessarily that you talked to the wrong experts or talked to too few of them. The problem was that you failed to do the most elementary thinking needed to see if what they were saying (or what you thought they were saying) in fact made any sense. If you were stupid, it wouldn’t be so bad to have messed up such elementary reasoning, but I don’t by any means think you are stupid. That makes the failure to do the thinking all the more disappointing. I will take Nathan Myhrvold’s claim about solar cells, which you quoted prominently in your book, as an example.
As quoted by you, Mr. Myhrvold claimed, in effect, that it was pointless to try to solve global warming by building solar cells, because they are black and absorb all the solar energy that hits them, but convert only some 12% to electricity while radiating the rest as heat, warming the planet. Now, maybe you were dazzled by Mr Myhrvold’s brilliance, but don’t we try to teach our students to think for themselves? Let’s go through the arithmetic step by step and see how it comes out. It’s not hard. Let’s do the thought experiment of building a solar array to generate the entire world’s present electricity consumption, and see what the extra absorption of sunlight by the array does to climate. First we need to find the electricity consumption. Just do a Google search on “World electricity consumption†and here you are:
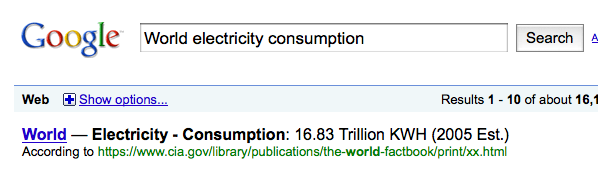
Now, that’s the total electric energy consumed during the year, and you can turn that into the rate of energy consumption (measured in Watts, just like the world was one big light bulb) by dividing kilowatt hours by the number of hours in a year, and multiplying by 1000 to convert kilowatts into watts. The answer is two trillion Watts, in round numbers. How much area of solar cells do you need to generate this? On average, about 200 Watts falls on each square meter of Earth’s surface, but you might preferentially put your cells in sunnier, clearer places, so let’s call it 250 Watts per square meter. With a 15% efficiency, which is middling for present technology the area you need is
2 trillion Watts/(.15 X 250. Watts per square meter) or 53,333 square kilometers. That’s a square 231 kilometers on a side, or about the size of a single cell of a typical general circulation model grid box. If we put it on the globe, it looks like this:

So already you should be beginning to suspect that this is a pretty trivial part of the Earth’s surface, and maybe unlikely to have much of an effect on the overall absorbed sunlight. In fact, it’s only 0.01% of the Earth’s surface. The numbers I used to do this calculation can all be found in Wikipedia, or even in a good paperbound World Almanac.
But we should go further,...
I am addressing this to you rather than your journalist-coauthor because one has become all too accustomed to tendentious screeds from media personalities (think Glenn Beck) with a reckless disregard for the truth. However, if it has come to pass that we can’t expect the William B. Ogden Distinguished Service Professor (and Clark Medalist to boot) at a top-rated department of a respected university to think clearly and honestly with numbers, we are indeed in a sad way.
By now there have been many detailed dissections of everything that is wrong with the treatment of climate in Superfreakonomics , but what has been lost amidst all that extensive discussion is how really simple it would have been to get this stuff right. The problem wasn’t necessarily that you talked to the wrong experts or talked to too few of them. The problem was that you failed to do the most elementary thinking needed to see if what they were saying (or what you thought they were saying) in fact made any sense. If you were stupid, it wouldn’t be so bad to have messed up such elementary reasoning, but I don’t by any means think you are stupid. That makes the failure to do the thinking all the more disappointing. I will take Nathan Myhrvold’s claim about solar cells, which you quoted prominently in your book, as an example.
As quoted by you, Mr. Myhrvold claimed, in effect, that it was pointless to try to solve global warming by building solar cells, because they are black and absorb all the solar energy that hits them, but convert only some 12% to electricity while radiating the rest as heat, warming the planet. Now, maybe you were dazzled by Mr Myhrvold’s brilliance, but don’t we try to teach our students to think for themselves? Let’s go through the arithmetic step by step and see how it comes out. It’s not hard. Let’s do the thought experiment of building a solar array to generate the entire world’s present electricity consumption, and see what the extra absorption of sunlight by the array does to climate. First we need to find the electricity consumption. Just do a Google search on “World electricity consumption†and here you are:

Now, that’s the total electric energy consumed during the year, and you can turn that into the rate of energy consumption (measured in Watts, just like the world was one big light bulb) by dividing kilowatt hours by the number of hours in a year, and multiplying by 1000 to convert kilowatts into watts. The answer is two trillion Watts, in round numbers. How much area of solar cells do you need to generate this? On average, about 200 Watts falls on each square meter of Earth’s surface, but you might preferentially put your cells in sunnier, clearer places, so let’s call it 250 Watts per square meter. With a 15% efficiency, which is middling for present technology the area you need is

So already you should be beginning to suspect that this is a pretty trivial part of the Earth’s surface, and maybe unlikely to have much of an effect on the overall absorbed sunlight. In fact, it’s only 0.01% of the Earth’s surface. The numbers I used to do this calculation can all be found in Wikipedia, or even in a good paperbound World Almanac.
But we should go further,...

ending with a Google map of how to get to his office to ask questions:
May I suggest that if you should happen to need some friendly help next time you take on the topic of climate change, or would like to have a chat about why aerosol geoengineering might not be a cure-all, or just need a critical but informed opponent to bounce ideas off of, you don’t have to go very far. For example…
But given the way Superfreakonomics mangled Ken Caldeira’s rather nuanced views on geoengineering, let’s keep it off the record, eh?
Your colleague,
Raymond T. Pierrehumbert
Louis Block Professor in the Geophysical Sciences
The University of Chicago

But given the way Superfreakonomics mangled Ken Caldeira’s rather nuanced views on geoengineering, let’s keep it off the record, eh?
Your colleague,
Raymond T. Pierrehumbert
Louis Block Professor in the Geophysical Sciences
The University of Chicago



 Fractal Design Arc Mini R2, 3800X, Asus B450M-PRO mATX, 2x8GB B-die@3800C16, AMD Vega64, Seasonic 850W Gold, Black Ice Nemesis/Laing DDC/EKWB 240 Loop (VRM>CPU>GPU), Noctua Fans.
Fractal Design Arc Mini R2, 3800X, Asus B450M-PRO mATX, 2x8GB B-die@3800C16, AMD Vega64, Seasonic 850W Gold, Black Ice Nemesis/Laing DDC/EKWB 240 Loop (VRM>CPU>GPU), Noctua Fans.

Comment